Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s actively transforming industries, automating tasks, and reshaping the global workforce. OpenAI, a pioneer in generative AI, has been at the forefront of this revolution with models like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Codex, among others. But as AI continues to advance, one of the most pressing questions remains: What does the future of jobs look like in an AI-driven world?
Some experts argue that AI will create new opportunities, automating repetitive tasks and allowing humans to focus on more meaningful work. Others fear widespread job displacement, particularly in knowledge-based industries. This article delves into how OpenAI is redefining employment, exploring the emerging job landscape, the impact of AI automation, and strategies for adapting to this new era.
The Evolution of AI in the Workplace
AI’s integration into the workforce has followed three major phases:
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks – From manufacturing robots to data-entry automation, AI has replaced mundane, rule-based jobs.
- Augmenting Human Work – AI models like ChatGPT assist professionals in content creation, coding, and customer support, enhancing productivity rather than replacing jobs outright.
- Autonomous AI Decision-Making – The rise of autonomous AI agents suggests a future where AI systems manage complex decision-making, potentially reducing reliance on human oversight.
OpenAI’s Role in Shaping the Future of Work
OpenAI has significantly influenced the evolution of AI-driven employment. Several key innovations highlight its impact:
1. Generative AI in Knowledge Work
OpenAI’s ChatGPT and DALL·E models have already redefined content creation, copywriting, graphic design, and even legal and financial advisory services. These models are automating content generation and assisting professionals in crafting high-quality work faster.
2. AI in Software Development
Codex, the AI model behind GitHub Copilot, has revolutionized software engineering. By auto-generating code snippets and assisting in debugging, AI enables developers to work more efficiently while shifting their focus to higher-level problem-solving.
3. AI-Augmented Customer Service
Businesses are increasingly deploying AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, reducing the need for traditional customer service representatives. While this automation may displace some entry-level positions, it is also creating demand for AI trainers, chatbot designers, and prompt engineers.
4. Reshaping Creative Industries
While traditional design and marketing roles face disruption, AI tools like DALL·E and Sora (OpenAI’s video generation model) are enabling new forms of creative expression. Artists, designers, and content creators are now leveraging AI to enhance productivity rather than being replaced outright.
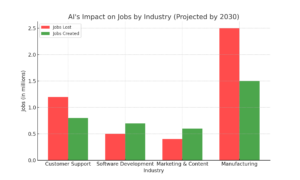
Data Insights: AI Job Disruption vs. Creation
While fears of AI-induced job losses persist, data from industry reports suggest a more nuanced reality:
| Industry | Jobs Lost to AI | Jobs Created by AI |
| Customer Support | 1.2M (Projected by 2030) | 800K AI trainers, chatbot managers |
| Software Development | 500K automated coding jobs | 700K AI-assisted development roles |
| Marketing & Content | 400K traditional copywriting jobs | 600K AI-enhanced creative roles |
| Manufacturing | 2.5M automation-based layoffs | 1.5M robotics and AI maintenance roles |
(Source: McKinsey Global Institute, World Economic Forum AI Jobs Report 2024)
Visualizing the Impact
To better understand how AI is affecting jobs across industries, the bar chart below compares projected job losses and job creation due to AI:
The chart illustrates that while AI may displace millions of jobs in sectors like manufacturing and customer support, it simultaneously creates new opportunities in AI-related fields.
The Rise of AI-Augmented Professions
Rather than eliminating jobs outright, AI is evolving the nature of work, leading to new professions:
- AI Trainers & Prompt Engineers – Specialists fine-tune AI models and optimize prompts for better outputs.
- Ethical AI Consultants – Experts help companies navigate responsible AI implementation.
- AI Workflow Integrators – Professionals focus on integrating AI systems into business processes.
- Human-AI Collaboration Managers – Roles dedicated to optimizing synergy between AI tools and human employees.
Strategies for Adapting to an AI-Driven Job Market
To thrive in an AI-powered workforce, professionals and businesses must adapt:
- Reskilling & Upskilling – Employees must develop AI literacy, focusing on data analysis, machine learning, and prompt engineering.
- Emphasizing Creativity & Critical Thinking – AI struggles with complex problem-solving, making human creativity indispensable.
- Leveraging AI as a Co-Pilot – Rather than competing with AI, workers should embrace it as an augmentation tool to enhance productivity.
- Regulatory & Ethical Considerations – Policymakers and businesses must develop frameworks to ensure fair AI implementation, preventing mass displacement.
Future Outlook: What’s Next for AI & Jobs?
While AI will undoubtedly reshape employment, its impact will likely follow historical technological shifts—eliminating some roles while creating new ones. OpenAI’s models exemplify this transition, demonstrating that AI can be a tool for augmentation rather than pure automation.
Looking ahead, AI’s future will depend on how businesses, governments, and individuals navigate its integration into the workforce. With proactive adaptation and a focus on reskilling, the AI revolution could lead to a more innovative and productive job market rather than one defined by displacement.
Conclusion
AI’s growing influence on employment is inevitable, but it presents both challenges and opportunities. OpenAI is at the center of this transformation, reshaping industries and redefining traditional job roles. While fears of job losses are valid, history suggests that technology, when managed effectively, leads to greater productivity, new career opportunities, and economic growth.
The key question remains: How will society harness AI’s potential while mitigating its risks? The answer will determine whether AI becomes a tool for progress or a force of disruption in the global workforce.


